Extensive information on risk management can be found in:
Our risk governance
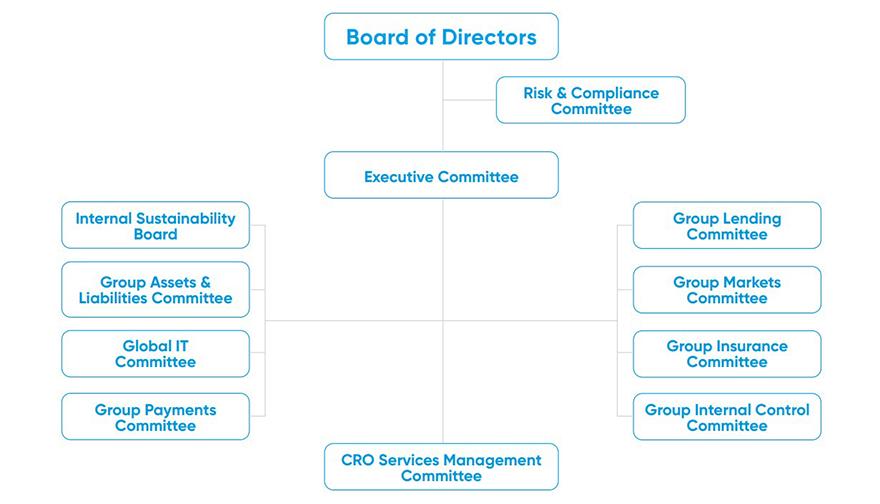
Our risk governance model includes the following main elements:
- The Board of Directors (Board), supported by the Risk & Compliance Committee, decides on the risk appetite – defining the group’s overall risk playing field and the risk strategy – and supervises KBC’s risk exposure in relation to this risk appetite. It is also accountable for having robust governance arrangements in place to ensure that all material risks of KBC Group are managed appropriately and for promoting a sound, consistent group-wide risk culture.
- The Risk & Compliance Committee (RCC) is an advisory committee that advises on topics for which the Board is accountable, such as the group’s risk appetite, the monitoring of risk exposure compared to the group’s risk appetite and the supervision of the implementation, efficiency and effectiveness of the Enterprise Risk Management Framework.
- The Executive Committee (ExCo) is the management committee responsible for integrating risk management, operating in alignment with decisions taken by the Board related to risk appetite, strategy, and performance goals.
- The ExCo is supported by the CRO Services Management Committee (CRO Services MC), risk committees and business.
We manage our risks using the ‘Three Lines of Defence’ model:
- Risk-aware business people act as the first Line of Defence for conducting sound risk management. This involves allocating sufficient priority and capacity to risk topics, performing the right controls in the right manner and making sure that the risk self-assessment of the business side is of a sufficiently high standard.
- In line with regulations, independent control functions, at both group and local level, act as (part of) the second Line of Defence:
- The risk function develops, imposes and monitors consistent implementation of the Enterprise Risk Management Framework, describing the processes, methods and approaches to identify, measure and report on risks and to define the risk appetite. To strengthen the voice of the risk function and to ensure that the decision-making bodies of the business entities are appropriately challenged on matters of risk management and receive expert advice, KBC has deployed independent Chief Risk Officers (CROs) throughout the group. Close collaboration with the business is assured since the independent CROs are present in management committees and take part in the local decision-making process, while their independence is achieved through a functional reporting line to the Group CRO. If necessary, they can exercise a right of veto.
- The compliance function’s prime objective is to prevent KBC from running a compliance risk (i.e. incurring loss or damage – regardless of its nature – due to noncompliance with applicable laws, regulations or internal rules) that falls either within the scope of the compliance function or within the areas assigned to it by the ExCo. The compliance function is characterized by its specific status, its place in the organization chart (Group Compliance, hierarchically under the CRO) and the associated reporting lines.
- The actuarial function ensures additional quality control by providing expert technical actuarial advice to the supervisory body, the RCC and the executive body of KBC Group, of KBC Insurance and all reinsurance and insurance entities within the group. Such advice covers the calculation of the technical provisions for insurance liabilities, the reinsurance policy and underwriting risk. As described in the ‘Actuarial Function Charter’, in order to safeguard independence, the actuarial function holder reports functionally to the Group CRO.
- Internal audit acts as the third Line of Defence. It is responsible for giving reasonable assurance to the Board that the overall internal control environment is effective, and that effective policies and processes are in place and applied consistently throughout the group.